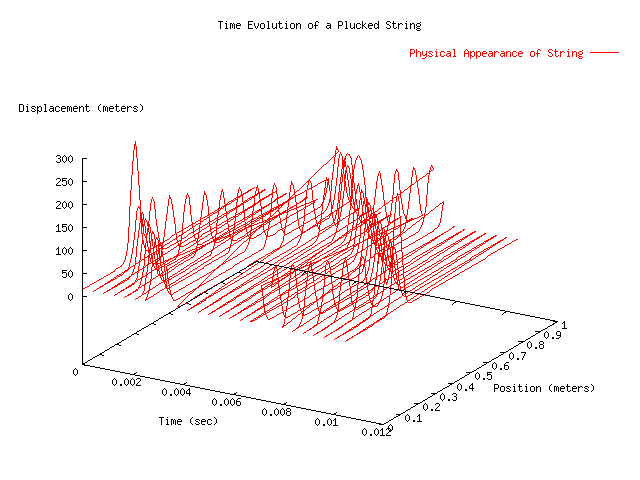
Answer for Problem 11
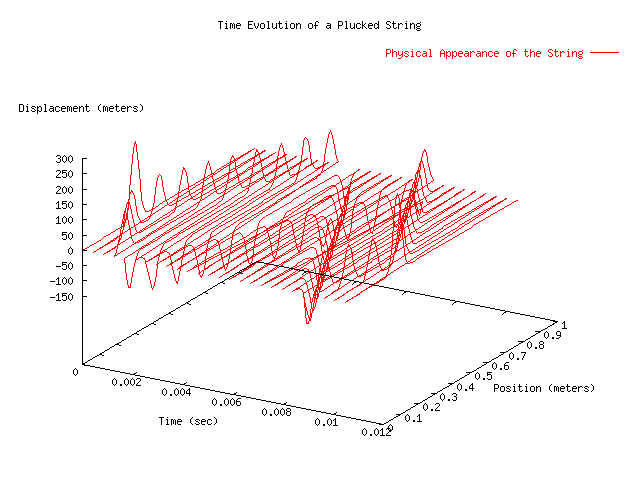
Using the FFT algorithms from Press, the time evolution of a plucked string was evaluated for a string that was fixed at the ends and one that was not. The below charts represent the data which came out of the program listed below.

#ifndef FUNCTION_H #define FUNCTION_H
#include <functional> #include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <time.h> #include <math.h>
using namespace std;
//
// The following group of classes were an attempt to develop a way to call functions on functions
//
class Function : public unary_function<double,double>
{
public:
Function() {};
virtual ~Function()
{
//do garbage collection on tempFunctions //crashes program?
for (vector<Function*>::iterator iter = tempFunctions.begin(); iter != tempFunctions.end(); iter++)
delete *iter;
};
virtual double operator()(double x){return x;};
virtual Function& operator^(Function& f);
virtual Function& operator*(Function& f);
virtual Function& operator+(Function& f);
virtual Function& operator-(Function& f);
virtual Function& operator()(Function& f);
virtual Function& operator^(double x); virtual Function& operator*(double x); virtual Function& operator+(double x); virtual Function& operator-(double x);
virtual Function& operator-();
virtual Function& getDerivative() { return *this;};
protected:
vector<Function*> tempFunctions;
};
class PowFunc : public Function
{
public:
PowFunc(Function&f1, Function& f2) : a(f1), b(f2) {}
virtual double operator() ( double x) { return pow(a(x),b(x));};
virtual Function& getDerivative();
protected: Function& a; Function& b; };
Function& Function::operator^(Function& f)
{
PowFunc* a;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (a = new PowFunc(*this, f)));
return *a;
};
Function& PowFunc::getDerivative()
{
cerr << "can not evaluate f(x)^g(x). Need to develop numerical approximation" <<endl;
return a*b;
};
class AdditionFunc : public Function
{
public:
AdditionFunc(Function&f1, Function& f2) : a(f1), b(f2) {}
virtual double operator() ( double x) { return (a(x)+b(x));};
virtual Function& getDerivative();
protected:
Function& a;
Function& b;
};
Function& Function::operator+(Function& f)
{
AdditionFunc* a;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (a = new AdditionFunc(*this, f)));
return *a;
};
Function& AdditionFunc::getDerivative()
{
return (a.getDerivative() + b.getDerivative());
};
class SubtractionFunc : public Function
{
public:
SubtractionFunc(Function&f1, Function& f2) : a(f1), b(f2) {}
virtual double operator() ( double x) { return (a(x)-b(x));};
virtual Function& getDerivative();
protected: Function& a; Function& b; };
Function& Function::operator-(Function& f)
{
SubtractionFunc* s;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (s = new SubtractionFunc(*this, f)));
return *s;
};
Function& SubtractionFunc::getDerivative()
{
return (a.getDerivative() - b.getDerivative());
};
class MultiplyFunc : public Function
{
public:
MultiplyFunc(Function& f1, Function& f2) :a(f1), b(f2) {};
virtual double operator() ( double x) { return a(x)*b(x);};
virtual Function& getDerivative();
protected: Function& a; Function& b; };
Function& Function::operator*(Function& f)
{
MultiplyFunc * m;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (m = new MultiplyFunc(*this, f)));
return *m;
};
Function& MultiplyFunc::getDerivative()
{
return (a.getDerivative()*b + a*b.getDerivative());
};
class CompositionFunc : public Function
{
public:
CompositionFunc(Function& f1, Function& f2) :a(f1), b(f2) {};
virtual double operator() ( double x) { return a(b(x));};
virtual Function& getDerivative();
protected:
Function& a;
Function& b;
};
Function& Function::operator()(Function& f)
{
CompositionFunc* c;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (c = new CompositionFunc(*this, f)));
return *c;
};
Function& CompositionFunc::getDerivative()
{
return (a.getDerivative()(b)*b.getDerivative());
};
class ConstFunc : public Function
{
public:
ConstFunc(double x) : _x(x) {};
virtual double operator()(double x){return _x;};
protected:
double _x;
};
class IdentityFunction : public ConstFunc
{
public:
IdentityFunction() : ConstFunc(1) {};
};
class VectorFunc : public Function
{
public:
VectorFunc(vector<double> &list) : v(list) {};
virtual double operator()(double n) { return v[(int)n]; };
protected:
vector<double> & v;
};
Function& Function::operator^(double x)
{
ConstFunc* c;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (c = new ConstFunc(x)));
return ((*this)^(*c));
}
Function& Function::operator*(double x)
{
ConstFunc* c;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (c = new ConstFunc(x)));
return ((*this)*(*c));
};
Function& Function::operator+(double x)
{
ConstFunc* c;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (c = new ConstFunc(x)));
return ((*this)+(*c));
}
;
Function& Function::operator-(double x)
{
ConstFunc* c;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (c = new ConstFunc(x)));
return ((*this)-(*c));
}
;
Function& Function::operator-()
{
ConstFunc* c;
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), (c = new ConstFunc(0)));
return ((*c) - (*this));
};
#define functor(NAME, FUNC) \
class NAME : public Function \
{\
public: \
virtual Function& operator()(Function& x) { return Function::operator ()(x);}; \
virtual double operator()(double x) { return FUNC(x);}; \
};
#define FunctionObject(FUNCTION) \ functor(FunctionObject##FUNCTION, FUNCTION) \ FunctionObject##FUNCTION FUNCTION##F;
#define FunctionObjectSpec(NAME, FUNCTION, OBJECT) \ functor(NAME,FUNCTION) \ NAME OBJECT;\
#define FunctionObjectSpecPtr(NAME, FUNCTION, OBJECT) \ functor(NAME,FUNCTION) \ NAME* OBJECT;\
#define FunctionObject_(NAME, FUNCTION) \ functor(NAME,FUNCTION) \ NAME FUNCTION##F;
FunctionObjectSpec(ExponentialFunc, exp, exponentialFunc);
FunctionObjectSpec(CosFunc, cos, cosFunc)
FunctionObjectSpec(SinFunc, sin, sinFunc);
class SumFunc : public Function
{
public:
enum Type {Int, Dub};
SumFunc(int lower, int upper, int increment = 1) : a(lower), b(upper), inc(increment), type(Int) {};
SumFunc(double lower, double upper, double increment = 1) : a(lower), b(upper), inc(increment), type(Dub){};
virtual double operator()(double x) { return ((b-a)/inc)*x; };
virtual Function& operator()(Function& f)
{
double val = 0;
for (double n = a;n<=b;n+=inc)
val += f(n);
ConstFunc *c = new ConstFunc(val);
tempFunctions.insert(tempFunctions.end(), c);
return *c;
};
protected: double a, b, inc; Type type; };
#endif
#include "Function.h" //#include <math.h> #include <vector>
const double pi = acos(-1); //From numerical recipies
void four11( vector<double>& data, const int isign)
{
//vector<complex<double> > ret(vals.size());
//#include <cmath>
//#include "nr.h"
//using namespace std;
//void NR: :four1(Vec_io_dp &data, const int isign)
// Replaces data [0. .2*nn-1] by its discrete Fourier transform, if isign is input as 1; or replaces
// data [0. .2*nn-1] by nn times its inverse discrete Fourier transform, if isign is input as -1.
// data is a complex array of length nn stored as a real array of length 2*nn. nn MUST be an
// integer power of 2 (this is not checked for!)
{
int n , mmax, m, j, istep, i;
double wtemp, wr, wpr, wpi, wi, theta, tempr, tempi;
int nn=data .size( )/2;
n=nn << 1;
j=1;
for (i=1; i<n; i+=2)
{
if (j>i)
{
swap (data [j-1], data [i-1]);
swap (data [j], data [i]) ;
}
m=nn;
while (m>=2 && j>m)
{
j-=m;
m>>=1;
}
j+=m;
}
mmax=2;
while (n>mmax)
{
istep=mmax << 1;
theta=isign*(6.28318530717959/mmax);
wtemp=sin (0.5*theta);
wpr = -2.0*wtemp*wtemp;
wpi = sin(theta);
wr=1.0;
wi=0.0;
for (m=1; m<mmax; m+=2)
{
for (i=m; i<n; i+=istep)
{
j=i+mmax;
tempr=wr*data [j-1] - wi*data [j];
tempi=wr*data [j] +wi*data [j-1];
data [j-1]=data [i-1] - tempr;
data [j] = data [i] - tempi;
data [i-1] += tempr;
data [i] += tempi;
}
wr=(wtemp=wr)*wpr-wi*wpi+wr;
wi=wi*wpr+wtemp*wpi+wi;
}
mmax=istep;
}
}
}
void four11real(vector<double>& data, const int isign)
{
int i, i1, i2, i3, i4;
double c1=0.5, c2, h1r, h1i, h2r, h2i, wr, wi, wpr, wpi, wtemp, theta;
int n=data. size ( );
theta=pi/(double)(n>>1);
if (isign == 1) {
c2 = -0.5;
four11 (data,1);
} else {
c2=0.5;
theta = -theta;
}
wtemp=sin (0.5*theta);
wpr = -2.0*wtemp*wtemp;
wpi =sin (theta);
wr=1.0+wpr;
wi=wpi;
for (i=1; i<(n>>2) ; i++) {
i2=1+(i1=i+i);
i4=1+(i3=n-i1);
h1r=c1*(data[i1] +data[i3] );
h1i=c1*(data [i2] - data [i4] );
h2r= -c2* (data [i2] +data [i4]);
h2i=c2* (data [i1] -data [i3] );
data [i1]=h1r+wr*h2r-wi*h2i;
data [i2] =h1i+wr*h2i+wi*h2r;
data [i3] =h1r-wr*h2r+wi*h2i;
data[i4] = -h1i+wr*h2i+wi*h2r;
wr= (wtemp+wr)*wpr-wi*wpi+wr;
wi=wi*wpr+wtemp*wpi+wi;
}
if (isign == 1) {
data [0] = (h1r=data [0]) +data [1];
data [1] = h1r-data [1];
} else {
data [0] =c1* ( ( h1r=data [0]) +data [1]);
data [1] =c1* (h1r-data [1] );
four11(data, -1);
}
}
void four11sin(vector<double>& y)
{
int j;
double sum, y1, y2, theta, wi=0.0, wr=1.0, wpi, wpr, wtemp;
int n=y. size ( );
theta=3.141592653589793238/(double)(n);
wtemp=sin (0.5*theta);
wpr=-2.0*wtemp*wtemp;
wpi=sin (theta);
y [0] = 0.0;
for (j=1; j<(n>>1)+1; j++)
{
wr=(wtemp=wr) *wpr-wi* wpi+wr;
wi=wi*wpr+wtemp*wpi+wi;
y1=wi*(y[j]+y [n-j]);
y2=0.5* (y[j] - y[n-j]);
y [j] =y1+y2;
y [n-j]=y1-y2;
}
four11real(y,1);
y [0]*=0.5;
sum=y [1] =0.0;
for (j=0; j<n-1; j+=2)
{
sum += y [j];
y [j]=y [j+1];
y [j+1]=sum;
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
double n = pow(2,9); //number of Fourier modes must be power of two
double xInc = 0.01; //the position increment on which to evaluate the string for time evolution double x0 = 0.3; //distance in meters plucked double k = 1000; //tension in the string 1/meters^2 double L = 1; //length of the string in meters double v = 300; //speed of the wave in meters/seconds double totalTime = pi/v; //seconds to evaluate the wave for double timeInc = totalTime/25; //the time increments used to generate the data (seconds) double x; //counter to evaluate initial pluck double t; //counter to evaluate time evolution int i;
Function self; FunctionObject(exp); Function& y = expF(((self-x0)^2)*(-k)); //function represting initial spatial disturbance due to pluck
//setup vector containing initial position of the string vector<double> vals(2*n); vector<double> vals2(2*n);
cout << "# The sample values of the string at the initial pluck is given by\n";
for (x=0,i=0;x<=L;x+=L/n)
{
vals[i*2] = y(x);
vals[i*2+1] = 0;
cout << x << "\t" << vals[2*i] << "\t" << vals[2*i+1] << endl;
i++;
};
vals2 = vals;
four11(vals, 1); //perform fourier transform on the values to get our coefficients an, bn
cout << "\n# The fourier spectrum is given by\n"; for (i=0;i<n;i++) cout << i << "\t" << vals[2*i] << "\t" << vals[2*i+1] << endl;
cout << "\n# The time evolved plot is given by\n";
for (t=0;t<=totalTime;t+=timeInc)
{
for (x=0;x<=L;x+=xInc)
{
double sum =0;
for (i=0;i<n/2;i++)
sum += (vals[i*2]*cos(2*i*pi*x/L) + vals[i*2+1]*sin(2*i*pi*x/L))*cos(2*i*v*t/L);
cout << t << "\t" << x << "\t" << sum << endl;
}
}
vals = vals2; four11sin(vals); cout << "\n# The fourier sin spectrum is given by\n"; for (i=0;i<n;i++) cout << i << "\t" << vals2[2*i] << "\t" << vals[2*i+1] << endl;
cout << "\n# The time evolved plot with the string held at both ends (fourier sin) is given by\n";
for (t=0;t<=totalTime;t+=timeInc)
{
for (x=0;x<=L;x+=xInc)
{
double sum =0;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
//sum += (vals[i*2]*cos(2*i*pi*x/L) + vals[i*2+1]*sin(2*i*pi*x/L))*cos(2*i*v*t/L);
sum += (vals[i]*sin(i*pi*x/L))*cos(2*i*v*t/L); //sine transform does not have a coefficients
cout << t << "\t" << x << "\t" << sum << endl; } } return 0; }