Answer for Assignment 4
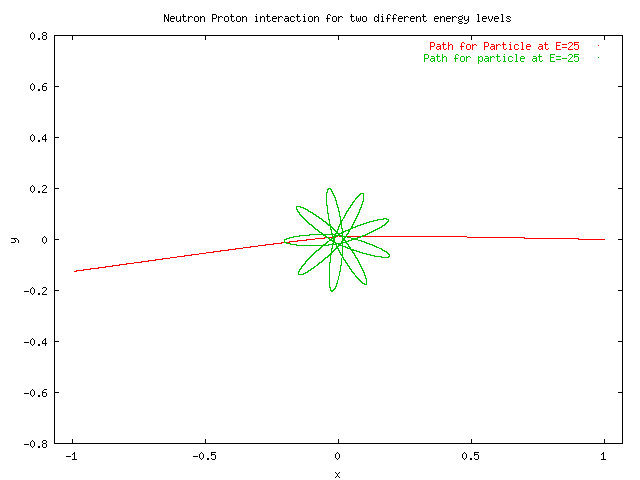
Below is the graph of the orbit of the conservative central force problem where U(r)=-ke^-r/a. These paths were plotted using a Simpson numerical integral approximation to evaluate theta by performing a preservation of angular momentum derived formula giving an equation for theta in terms of an integral from an initial radius to the radius for which one wishes to determine theta.

#include <functional> #include <iostream> #include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const double pi = acos(-1);
class Function : public unary_function<double,double>
{
public:
Function() {};
virtual result_type operator()(argument_type x){return x;};
virtual Function& getDerivative() { return *this;};
};
class ProtonNeutronFunc : public Function
{
public:
ProtonNeutronFunc(double factor, double exponent_factor, double angular, double energy)
:k(factor), a(exponent_factor), m(angular), E(energy)
{};
virtual result_type operator()(argument_type x)
{
return -1*k*exp(-1*x/a) + m/pow(x,2) - E;
};
protected: double k; double a; double m; double E;
};
class ThetaOfR : public ProtonNeutronFunc
{
public:
ThetaOfR(double factor, double exponent_factor, double angular, double energy)
: ProtonNeutronFunc(factor, exponent_factor, angular, energy)
{};
virtual result_type operator()(argument_type x)
{
return 2*m / ((x*x)*sqrt(4*m*( 0-ProtonNeutronFunc::operator ()(x) ) ) );
};
};
class Approximation
{
public:
Approximation(double lowerBound, double upperBound, Function& function)
:a(lowerBound), b(upperBound), f(function)
{};
virtual double calculate(double precision, int maxTries = 3000)
{
cout << "Default approximation not implemented" << endl;
return -1;
}
protected: double a; double b; Function& f; };
class SimpsonsApproximation : public Approximation
{
public:
SimpsonsApproximation(double lowerBound, double upperBound, Function & function)
: Approximation(lowerBound, upperBound,function)
{
if (a >=b) cerr << "Lowerbound " << a << " is greater than or equal to upper bound " << b << endl;
};
virtual double calculate(double precision, int maxTries=50)
{
double i, sum0;
double h = (b-a)/3;
double se= f(a+2*h), so = f(a+h) + f(b-h), sd = f(a) + f(b);
double sum = h*(sd + 2*se + 4*so)/3;
if (h <= 0) return 0;
do
{
h/=2;
sum0 = sum;
se+=so;
so =0;
for (i = a+h; i < b; i+=2*h)
so+=f(i);
sum = h*(sd + 2*se +4*so)/3;
//cout << sd << "\t" << se << "\t" << so << "\t" << sum << endl;
} while ((fabs((sum - sum0)/sum0) > precision) && (maxTries--));
return sum;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
ThetaOfR func25(70, 0.2, 0.01, 25);
ThetaOfR funcneg25(70, 0.2, 0.01, -25);
double r = 0, rmin=0.010458; double theta, thetaN;
cout.precision(16); cout << "# Welcome to the Simpson numerical integral approximation program for the Neutron-Proton Derivative" << endl; cout << "# for E=25 theta(r) = " << endl;
SimpsonsApproximation total25(rmin, 1, func25); thetaN=total25.calculate(0.0001);
for (r=1;r >=rmin;r-=0.001)//*log(r/rmin))
{
SimpsonsApproximation sp(r, 1, func25);
theta = sp.calculate(0.00001);
cout << r*cos(theta) << "\t" << r*sin(theta) <<endl;
cout << r*cos(2*thetaN - theta) << "\t" << r*sin(2*thetaN - theta) << endl;
}
cout << endl << "# for E=-25" << endl;
SimpsonsApproximation totalneg25(0.0158798, 0.204010, funcneg25); thetaN=totalneg25.calculate(0.00001);
for (r=0.0158798;r <= 0.204011;r+=0.0002)
{
SimpsonsApproximation sp(0.0158797, r, funcneg25);
//cout << r << "\t" << funcneg25(r) << endl;
theta = sp.calculate(0.00001);
for (int i =0;i<18;i+=2)
{
cout << r*cos(i*thetaN + theta) << "\t" << r*sin(i*thetaN + theta) <<endl;
cout << r*cos((i+2)*thetaN-theta) << "\t" << r*sin((i+2)*thetaN-theta) << endl;
}
}
return 0; }
GNUplot script file: